面试官:说说你对树的理解?相关的操作有哪些?
一、是什么
在计算机领域,树形数据结构是一类重要的非线性数据结构,可以表示数据之间一对多的关系。以树与二叉树最为常用,直观看来,树是以分支关系定义的层次结构
二叉树满足以下两个条件:
- 本身是有序树
- 树中包含的各个结点的不能超过 2,即只能是 0、1 或者 2
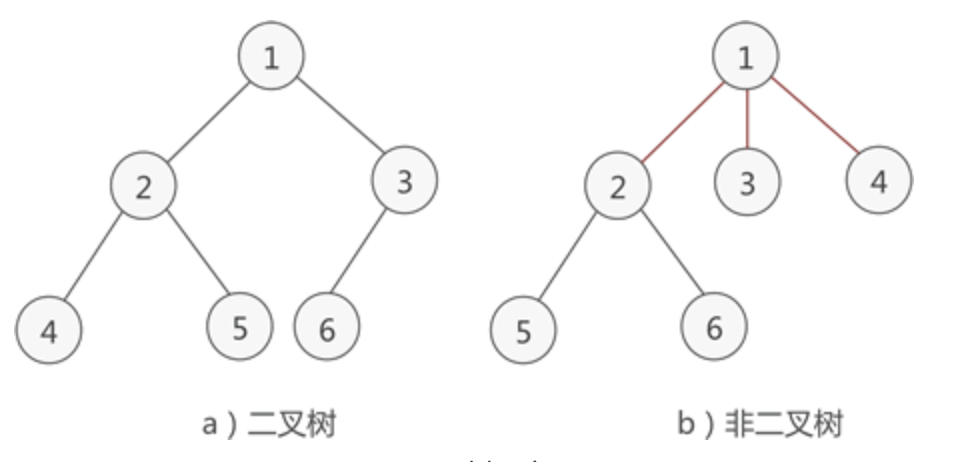
如下图,左侧的为二叉树,而右侧的因为头结点的子结点超过2,因此不属于二叉树:
同时,二叉树可以继续进行分类,分成了满二叉树和完成二叉树:
- 满二叉树:如果二叉树中除了叶子结点,每个结点的度都为 2
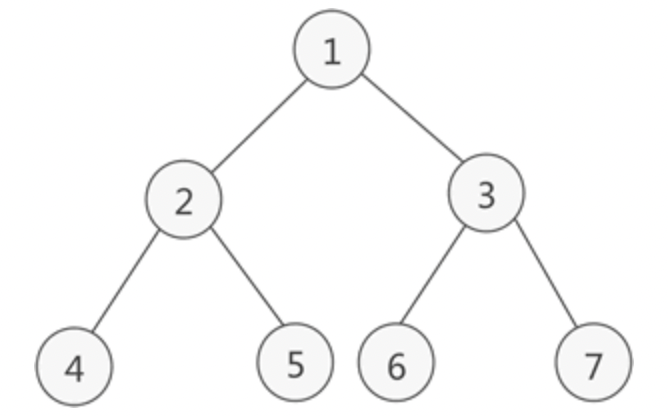
- 完成二叉树:如果二叉树中除去最后一层节点为满二叉树,且最后一层的结点依次从左到右分布

二、操作
关于二叉树的遍历,常见的有:
前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历
层序遍历
前序遍历
前序遍历的实现思想是:
- 访问根节点
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 若当前节点无左子树,则访问当前节点的右子
根据遍历特性,递归版本用代码表示则如下:
js
const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
console.log(root)
preOrder(root.left)
preOrder(root.right)
}const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
console.log(root)
preOrder(root.left)
preOrder(root.right)
}如果不使用递归版本,可以借助栈先进后出的特性实现,先将根节点压入栈,再分别压入右节点和左节点,直到栈中没有元素,如下:
js
const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
if (n.right) {
stack.push(n.right)
}
if (n.left) {
stack.push(n.left)
}
}
}const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
if (n.right) {
stack.push(n.right)
}
if (n.left) {
stack.push(n.left)
}
}
}中序遍历
前序遍历的实现思想是:
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 访问根节点
- 访问当前节点的右子
递归版本很好理解,用代码表示则如下:
js
const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
inOrder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inOrder(root.right)
}const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
inOrder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inOrder(root.right)
}非递归版本也是借助栈先进后出的特性,可以一直首先一直压入节点的左元素,当左节点没有后,才开始进行出栈操作,压入右节点,然后有依次压入左节点,如下:
js
const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
const stack = [root]
let p = root
while(stack.length || p){
while (p) {
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
p = n.right
}
}const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
const stack = [root]
let p = root
while(stack.length || p){
while (p) {
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
p = n.right
}
}后序遍历
前序遍历的实现思想是:
- 访问当前节点的左子树
- 访问当前节点的右子
- 访问根节点
递归版本,用代码表示则如下:
js
const postOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
postOrder(root.left)
postOrder(root.right)
console.log(n.val)
}const postOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return }
postOrder(root.left)
postOrder(root.right)
console.log(n.val)
}后序遍历非递归版本实际根全序遍历是逆序关系,可以再多创建一个栈用来进行输出,如下:
js
const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
const stack = [root]
const outPut = []
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
outPut.push(n.val)
if (n.right) {
stack.push(n.right)
}
if (n.left) {
stack.push(n.left)
}
}
while (outPut.length) {
const n = outPut.pop()
console.log(n.val)
}
}const preOrder = (root) => {
if(!root){ return }
const stack = [root]
const outPut = []
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
outPut.push(n.val)
if (n.right) {
stack.push(n.right)
}
if (n.left) {
stack.push(n.left)
}
}
while (outPut.length) {
const n = outPut.pop()
console.log(n.val)
}
}层序遍历
按照二叉树中的层次从左到右依次遍历每层中的结点
借助队列先进先出的特性,从树的根结点开始,依次将其左孩子和右孩子入队。而后每次队列中一个结点出队,都将其左孩子和右孩子入队,直到树中所有结点都出队,出队结点的先后顺序就是层次遍历的最终结果
用代码表示则如下:
js
const levelOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return [] }
const queue = [[root, 0]]
const res = []
while (queue.length) {
const n = queue.shift()
const [node, leval] = n
if (!res[leval]) {
res[leval] = [node.val]
} else {
res[leval].push(node.val)
}
if (node.left) { queue.push([node.left, leval + 1]) }
if (node.right) { queue.push([node.right, leval + 1]) }
}
return res
};const levelOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) { return [] }
const queue = [[root, 0]]
const res = []
while (queue.length) {
const n = queue.shift()
const [node, leval] = n
if (!res[leval]) {
res[leval] = [node.val]
} else {
res[leval].push(node.val)
}
if (node.left) { queue.push([node.left, leval + 1]) }
if (node.right) { queue.push([node.right, leval + 1]) }
}
return res
};三、总结
树是一个非常重要的非线性结构,其中二叉树以二叉树最常见,二叉树的遍历方式可以分成前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
同时,二叉树又分成了完成二叉树和满二叉树