面试官:双向数据绑定是什么
一、什么是双向绑定
我们先从单向绑定切入单向绑定非常简单,就是把Model绑定到View,当我们用JavaScript代码更新Model时,View就会自动更新双向绑定就很容易联想到了,在单向绑定的基础上,用户更新了View,Model的数据也自动被更新了,这种情况就是双向绑定举个栗子
当用户填写表单时,View的状态就被更新了,如果此时可以自动更新Model的状态,那就相当于我们把Model和View做了双向绑定关系图如下
二、双向绑定的原理是什么
我们都知道 Vue 是数据双向绑定的框架,双向绑定由三个重要部分构成
- 数据层(Model):应用的数据及业务逻辑
- 视图层(View):应用的展示效果,各类UI组件
- 业务逻辑层(ViewModel):框架封装的核心,它负责将数据与视图关联起来
而上面的这个分层的架构方案,可以用一个专业术语进行称呼:MVVM这里的控制层的核心功能便是 “数据双向绑定” 。自然,我们只需弄懂它是什么,便可以进一步了解数据绑定的原理
理解ViewModel
它的主要职责就是:
- 数据变化后更新视图
- 视图变化后更新数据
当然,它还有两个主要部分组成
- 监听器(Observer):对所有数据的属性进行监听
- 解析器(Compiler):对每个元素节点的指令进行扫描跟解析,根据指令模板替换数据,以及绑定相应的更新函数
三、实现双向绑定
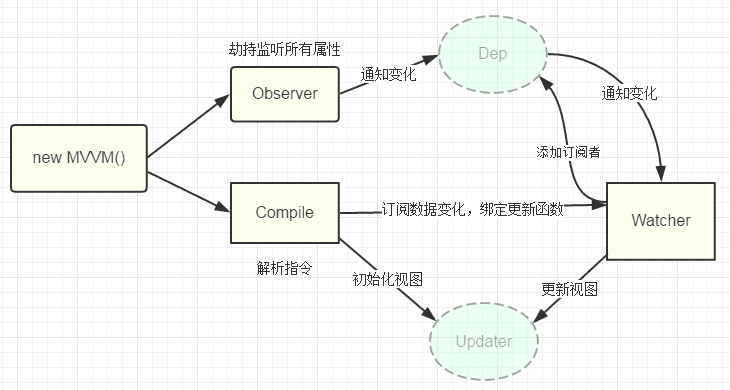
我们还是以Vue为例,先来看看Vue中的双向绑定流程是什么的
new Vue()首先执行初始化,对data执行响应化处理,这个过程发生在Observe中- 同时对模板执行编译,找到其中动态绑定的数据,从
data中获取并初始化视图,这个过程发生在Compile中 - 同时定义⼀个更新函数和
Watcher,将来对应数据变化时Watcher会调用更新函数 - 由于
data的某个key在⼀个视图中可能出现多次,所以每个key都需要⼀个管家Dep来管理多个Watcher - 将来data中数据⼀旦发生变化,会首先找到对应的
Dep,通知所有Watcher执行更新函数
流程图如下:
实现
先来一个构造函数:执行初始化,对data执行响应化处理
js
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options;
this.$data = options.data;
// 对data选项做响应式处理
observe(this.$data);
// 代理data到vm上
proxy(this);
// 执行编译
new Compile(options.el, this);
}
}class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options;
this.$data = options.data;
// 对data选项做响应式处理
observe(this.$data);
// 代理data到vm上
proxy(this);
// 执行编译
new Compile(options.el, this);
}
}对data选项执行响应化具体操作
js
function observe(obj) {
if (typeof obj !== "object" || obj == null) {
return;
}
new Observer(obj);
}
class Observer {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.walk(value);
}
walk(obj) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key]);
});
}
}function observe(obj) {
if (typeof obj !== "object" || obj == null) {
return;
}
new Observer(obj);
}
class Observer {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.walk(value);
}
walk(obj) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key]);
});
}
}编译Compile
对每个元素节点的指令进行扫描跟解析,根据指令模板替换数据,以及绑定相应的更新函数
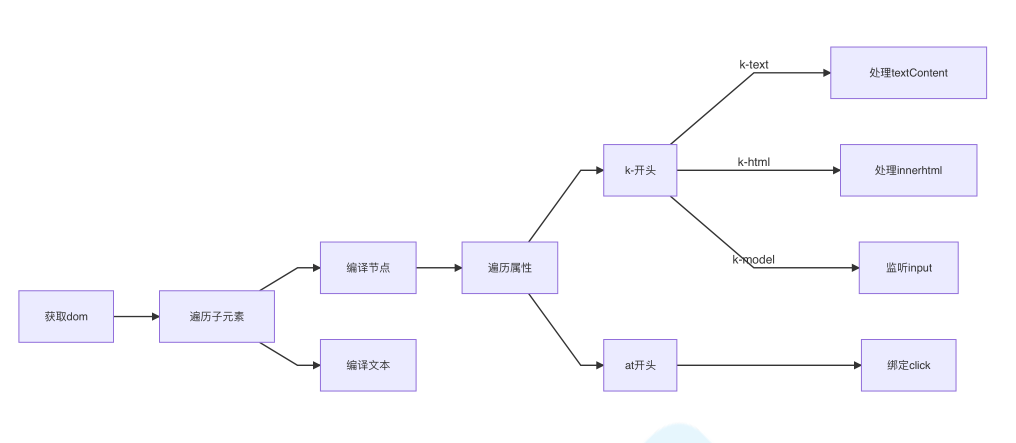
js
class Compile {
constructor(el, vm) {
this.$vm = vm;
this.$el = document.querySelector(el); // 获取dom
if (this.$el) {
this.compile(this.$el);
}
}
compile(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes;
Array.from(childNodes).forEach((node) => { // 遍历子元素
if (this.isElement(node)) { // 判断是否为节点
console.log("编译元素" + node.nodeName);
} else if (this.isInterpolation(node)) {
console.log("编译插值⽂本" + node.textContent); // 判断是否为插值文本 {{}}
}
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) { // 判断是否有子元素
this.compile(node); // 对子元素进行递归遍历
}
});
}
isElement(node) {
return node.nodeType == 1;
}
isInterpolation(node) {
return node.nodeType == 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.textContent);
}
}class Compile {
constructor(el, vm) {
this.$vm = vm;
this.$el = document.querySelector(el); // 获取dom
if (this.$el) {
this.compile(this.$el);
}
}
compile(el) {
const childNodes = el.childNodes;
Array.from(childNodes).forEach((node) => { // 遍历子元素
if (this.isElement(node)) { // 判断是否为节点
console.log("编译元素" + node.nodeName);
} else if (this.isInterpolation(node)) {
console.log("编译插值⽂本" + node.textContent); // 判断是否为插值文本 {{}}
}
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) { // 判断是否有子元素
this.compile(node); // 对子元素进行递归遍历
}
});
}
isElement(node) {
return node.nodeType == 1;
}
isInterpolation(node) {
return node.nodeType == 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.textContent);
}
}依赖收集
视图中会用到data中某key,这称为依赖。同⼀个key可能出现多次,每次都需要收集出来用⼀个Watcher来维护它们,此过程称为依赖收集多个Watcher需要⼀个Dep来管理,需要更新时由Dep统⼀通知
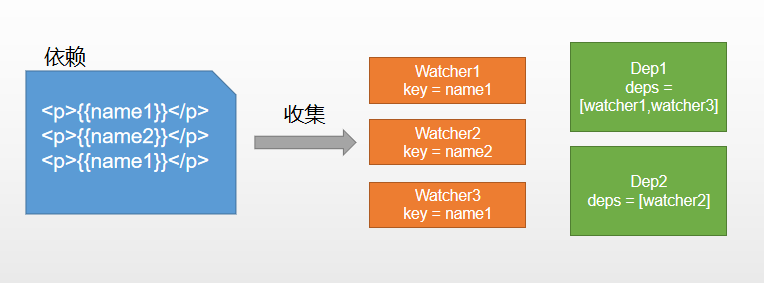
实现思路
defineReactive时为每⼀个key创建⼀个Dep实例- 初始化视图时读取某个
key,例如name1,创建⼀个watcher1 - 由于触发
name1的getter方法,便将watcher1添加到name1对应的Dep中 - 当
name1更新,setter触发时,便可通过对应Dep通知其管理所有Watcher更新
js
// 负责更新视图
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, updater) {
this.vm = vm
this.key = key
this.updaterFn = updater
// 创建实例时,把当前实例指定到Dep.target静态属性上
Dep.target = this
// 读一下key,触发get
vm[key]
// 置空
Dep.target = null
}
// 未来执行dom更新函数,由dep调用的
update() {
this.updaterFn.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key])
}
}// 负责更新视图
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, updater) {
this.vm = vm
this.key = key
this.updaterFn = updater
// 创建实例时,把当前实例指定到Dep.target静态属性上
Dep.target = this
// 读一下key,触发get
vm[key]
// 置空
Dep.target = null
}
// 未来执行dom更新函数,由dep调用的
update() {
this.updaterFn.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key])
}
}声明Dep
js
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.deps = []; // 依赖管理
}
addDep(dep) {
this.deps.push(dep);
}
notify() {
this.deps.forEach((dep) => dep.update());
}
}class Dep {
constructor() {
this.deps = []; // 依赖管理
}
addDep(dep) {
this.deps.push(dep);
}
notify() {
this.deps.forEach((dep) => dep.update());
}
}创建watcher时触发getter
js
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, updateFn) {
Dep.target = this;
this.vm[this.key];
Dep.target = null;
}
}class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, updateFn) {
Dep.target = this;
this.vm[this.key];
Dep.target = null;
}
}依赖收集,创建Dep实例
js
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
this.observe(val);
const dep = new Dep();
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target);// Dep.target也就是Watcher实例
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) return;
dep.notify(); // 通知dep执行更新方法
},
});
}function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
this.observe(val);
const dep = new Dep();
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target);// Dep.target也就是Watcher实例
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) return;
dep.notify(); // 通知dep执行更新方法
},
});
}